Statute
The Statute of InfoCamere voted by the Extraordinary Meeting of Shareholders is made up of a total of 33 articles, subdivided as follows:
- Name, headquarters, duration and object
- Partnership capital and partners of the company
- Meeting of Shareholders, Board of Directors, Comparable Control
- Legal auditing of accounts, manager in charge of preparing the corporate accounting documents and Board of Auditors
- Financial statement
- Withdrawal and exclusion of partners
- Dissolution of the company
- Controversies
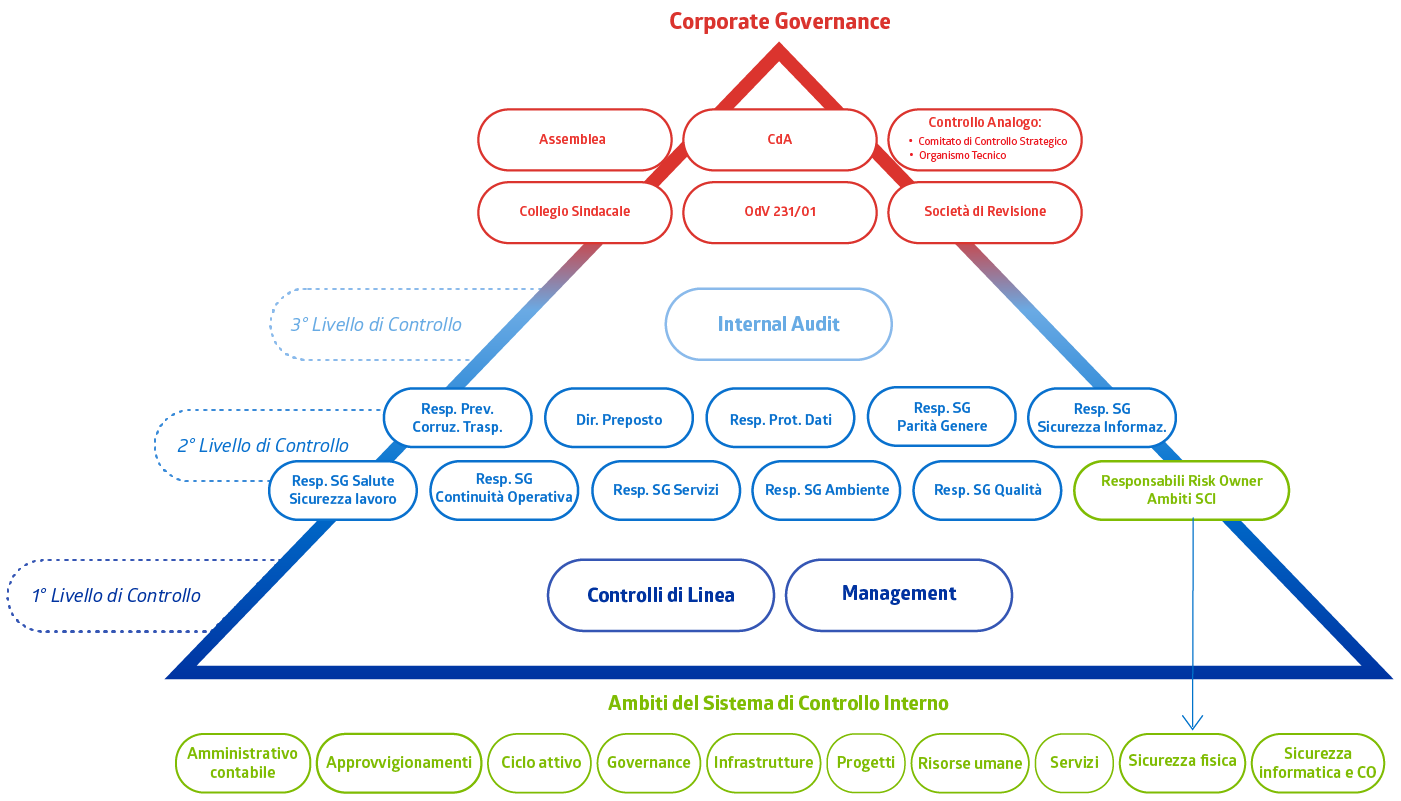
Control and risk management system